Maritime empires ap world history definition – In the annals of AP World History, the term “maritime empires” holds a pivotal place, referring to vast empires that wielded control over vast expanses of the world’s oceans. These empires left an enduring mark on global history, shaping political boundaries, economic systems, and cultural heritage.
Maritime empires emerged due to a confluence of factors, including technological advancements in shipbuilding and navigation, as well as the desire for trade, resources, and territorial expansion. They played a crucial role in the exchange of ideas, technologies, and religions, fostering cultural and social transformations.
Definition of Maritime Empires
Maritime empires are political entities that establish and maintain control over vast areas of the sea and the territories adjacent to them. They are characterized by their naval power, which allows them to project force and influence over distant regions.
Maritime empires have played a significant role in world history, shaping the political, economic, and cultural landscape of the globe.
Some notable examples of maritime empires include:
- Phoenician Empire (1200-539 BCE)
- Carthaginian Empire (814-146 BCE)
- Roman Empire (27 BCE-476 CE)
- Byzantine Empire (330-1453 CE)
- Venetian Republic (697-1797 CE)
- Genoese Republic (1000-1797 CE)
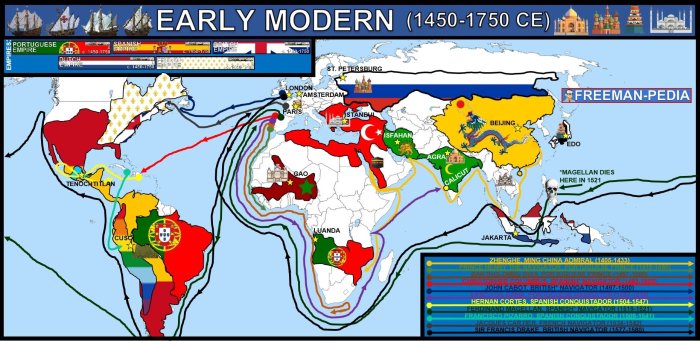
- Portuguese Empire (1415-1999 CE)
- Spanish Empire (1492-1975 CE)
- Dutch Empire (1581-1800 CE)
- British Empire (1583-1947 CE)
- French Empire (1604-1962 CE)
Rise of Maritime Empires: Maritime Empires Ap World History Definition
The rise of maritime empires was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Technological advancements in shipbuilding and navigation, which allowed for longer and more efficient voyages.
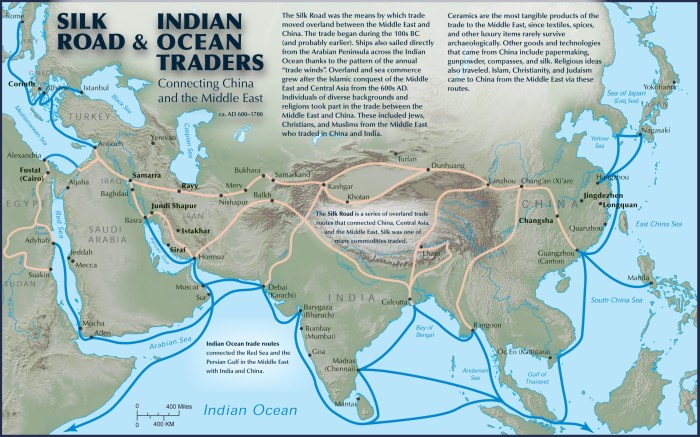
- The development of trade networks that connected different regions of the world, creating incentives for exploration and expansion.
- Political and economic instability in Europe, which led to the rise of ambitious and expansionist rulers.
Economic Impact of Maritime Empires
Maritime empires had a profound economic impact on their home countries and the regions they controlled:
- Trade: Maritime empires established extensive trade networks that connected different parts of the world, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas.
- Resource extraction: Maritime empires often established colonies in distant lands to exploit natural resources, such as minerals, timber, and agricultural products.
- Colonization: Maritime empires established colonies in various parts of the world, which provided them with access to new markets, resources, and labor.
Cultural and Social Impact of Maritime Empires
Maritime empires had a significant cultural and social impact on the people they encountered:
- Exchange of ideas: Maritime empires facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and religions between different cultures.
- Spread of Christianity: European maritime empires played a major role in the spread of Christianity to different parts of the world.
- Cultural assimilation: In some cases, maritime empires imposed their own cultural values and practices on the people they conquered.
Political and Military Impact of Maritime Empires
Maritime empires had a profound political and military impact on global affairs:
- Naval power: Maritime empires relied heavily on their naval power to project force and influence over distant regions.
- Diplomacy: Maritime empires engaged in diplomacy to establish alliances, secure trade agreements, and resolve conflicts.
- Territorial expansion: Maritime empires expanded their territories through conquest, colonization, and the establishment of protectorates.
Decline of Maritime Empires
The decline of maritime empires was caused by a variety of factors:
- Internal instability: Internal conflicts, political instability, and economic decline weakened maritime empires from within.
- External threats: Maritime empires faced threats from rival powers, both European and non-European, which challenged their dominance.
- Economic challenges: The rise of industrialization and the development of new technologies led to the decline of the traditional maritime trade routes.
Legacy of Maritime Empires

The legacy of maritime empires is still evident in the modern world:
- Political boundaries: The boundaries of many modern states were shaped by the expansion and decline of maritime empires.
- Economic systems: The global economic system was influenced by the trade networks established by maritime empires.
- Cultural heritage: The cultural heritage of many regions of the world was shaped by the interactions with maritime empires.
Question Bank
What is the key characteristic of a maritime empire?
A maritime empire possesses a dominant naval power and extensive control over sea routes and coastal territories.
What were the major factors that led to the rise of maritime empires?
Technological advancements in shipbuilding and navigation, economic motivations for trade and resource extraction, and political ambitions for territorial expansion.
How did maritime empires impact the cultural landscape of the world?
They facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and religions, leading to cultural diffusion and the emergence of new cultural identities.