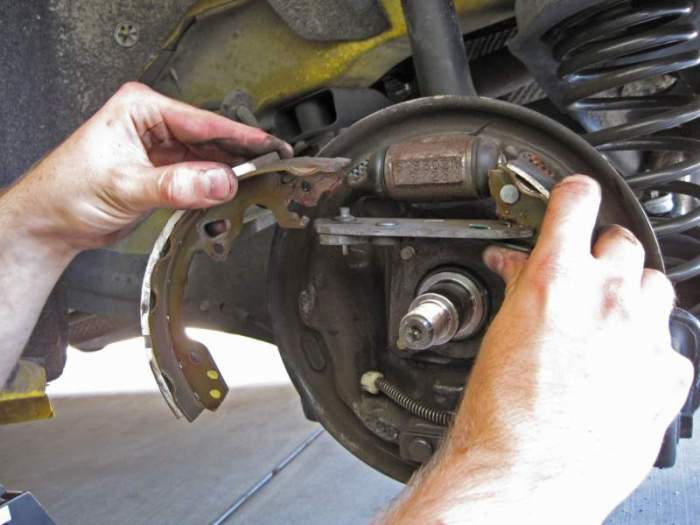
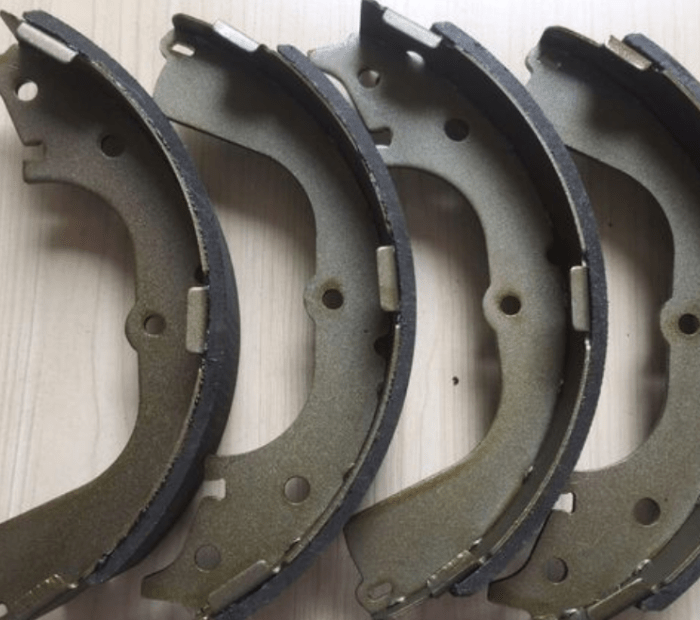
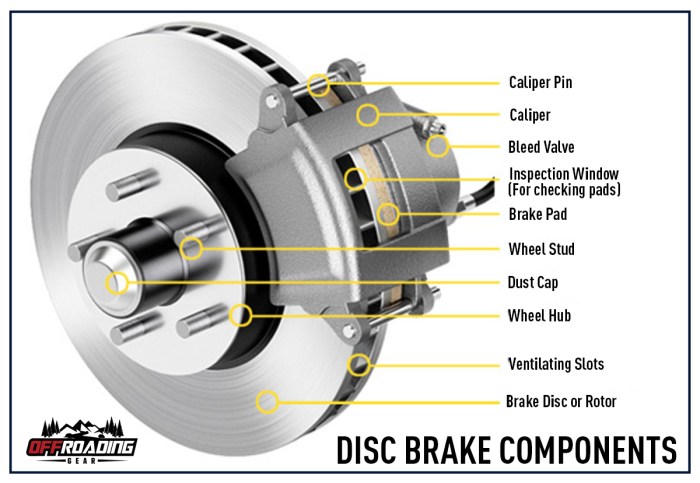
Brake shoes stop a car by exerting pressure on the brake drum or disc, creating friction that slows down or stops the vehicle. This fundamental mechanism, coupled with the various types of brake shoes and their applications, forms the cornerstone of automotive braking systems.
Understanding the relationship between pressure and braking efficiency, as well as the factors influencing brake shoe effectiveness, is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Regular maintenance and inspection of brake shoes are essential to prevent wear and potential malfunctions, while technological advancements continue to enhance braking capabilities and safety measures.
Brake Shoes: Mechanism and Efficiency
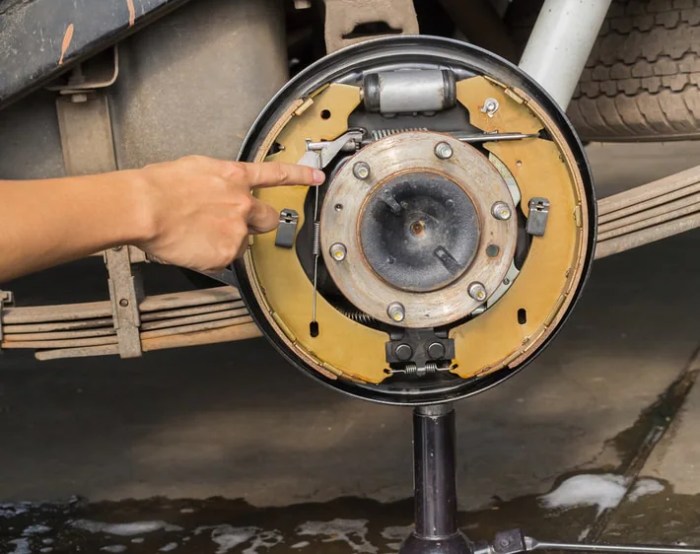

Brake shoes are essential components of automotive braking systems, responsible for generating friction and stopping a car by applying pressure against the brake drums.
Mechanism of Brake Shoes
Brake shoes are curved, metallic pads mounted on a backing plate. When the driver applies pressure to the brake pedal, hydraulic or mechanical force is transmitted to the brake shoes, causing them to expand outward and press against the inner surface of the brake drum.
This friction between the brake shoes and the drum creates a resistance that slows down and eventually stops the vehicle.
Types of Brake Shoes
Brake shoes vary in materials, designs, and applications:
- Organic brake shoes:Made from a blend of rubber, resins, and fibers, offering low noise and reduced brake fade.
- Metallic brake shoes:Comprised of iron, copper, or steel, providing high friction and durability but prone to noise and dust.
- Semi-metallic brake shoes:A combination of organic and metallic materials, offering a balance of performance and durability.
- Ceramic brake shoes:Made from ceramic compounds, offering exceptional heat resistance and long-lasting performance.
Pressure Exertion and Braking Efficiency
The effectiveness of brake shoes is directly influenced by the pressure they exert against the brake drum:
- Greater pressure:Increases friction and braking efficiency.
- Lesser pressure:Reduces friction and braking efficiency.
Factors influencing brake shoe effectiveness include shoe material, drum surface condition, and brake system design.
Brake Shoe Wear and Maintenance, Brake shoes stop a car by exerting pressure on the
Brake shoes experience wear over time due to friction and heat:
- Causes of wear:Excessive braking, contaminated brake fluid, misaligned wheels.
- Maintenance guidelines:Regular inspection, replacement when worn down to a specified thickness, cleaning of brake components.
Safety Considerations
Worn or malfunctioning brake shoes can pose significant safety risks:
- Reduced braking efficiency:Longer stopping distances, increased risk of accidents.
- Uneven wear:Can cause the vehicle to pull to one side while braking.
- Overheating:Can lead to brake fade and loss of control.
Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in brake shoe technology have improved braking performance and safety:
- Anti-lock braking systems (ABS):Prevent wheel lock-up during braking, enhancing control and stability.
- Electronic brake force distribution (EBD):Distributes braking force optimally across all wheels, improving braking efficiency.
- Advanced brake shoe materials:Ceramic and semi-metallic brake shoes offer enhanced durability and heat resistance.
Question Bank: Brake Shoes Stop A Car By Exerting Pressure On The
What is the primary function of brake shoes?
Brake shoes are designed to create friction against the brake drum or disc, slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
What factors influence the effectiveness of brake shoes?
Factors such as the coefficient of friction, surface area, and applied pressure impact the effectiveness of brake shoes.
Why is regular maintenance of brake shoes important?
Regular maintenance helps detect and prevent wear, ensuring optimal braking performance and safety.