A flat EEG is a good indication of deep sleep, a state characterized by slow brain waves and minimal activity. This distinctive EEG pattern provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of the brain during its most profound slumber.
During deep sleep, the brain undergoes a remarkable transformation, transitioning from the rapid, low-amplitude waves of REM sleep to the slow, high-amplitude delta waves associated with deep sleep. This shift is evident in the EEG recording, which displays a flattening of the waveform, indicating reduced brain activity.
1. Definition of Flat EEG and Deep Sleep
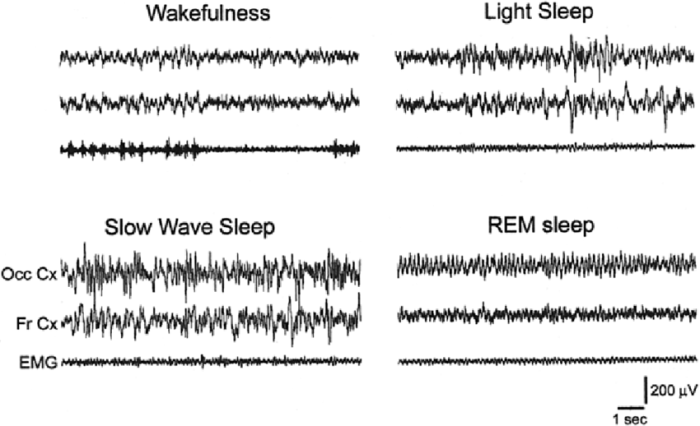
A flat electroencephalogram (EEG) is a recording of brain activity that shows little to no electrical activity. It is typically associated with deep sleep, the most restful stage of sleep. During deep sleep, the brain’s electrical activity slows down significantly, resulting in a flat EEG pattern.
2. Relationship between Flat EEG and Deep Sleep
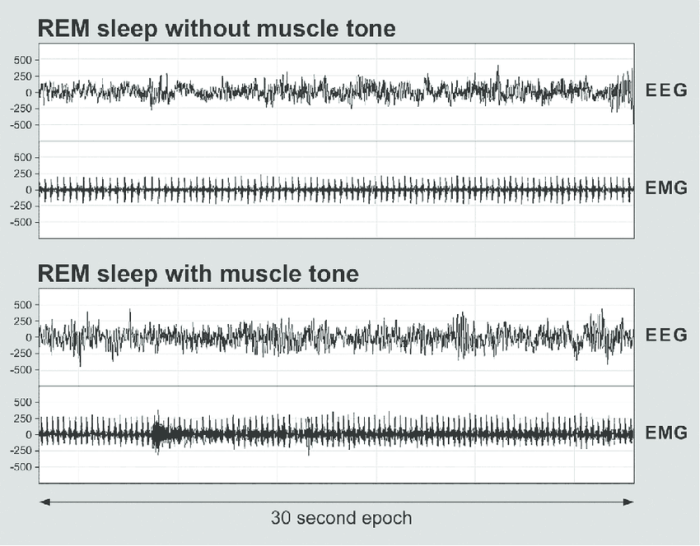
There is strong evidence supporting the correlation between a flat EEG and deep sleep. Studies have shown that as individuals enter deep sleep, their EEG patterns gradually flatten, indicating a decrease in brain activity. Conversely, when individuals awaken from deep sleep, their EEG patterns become more active, showing an increase in brain activity.
The physiological mechanisms underlying this relationship are not fully understood, but it is believed that the decrease in brain activity during deep sleep is related to a reduction in neural firing rates and synaptic activity. This decrease in neural activity leads to a decrease in electrical activity, resulting in a flat EEG pattern.
3. Limitations and Exceptions
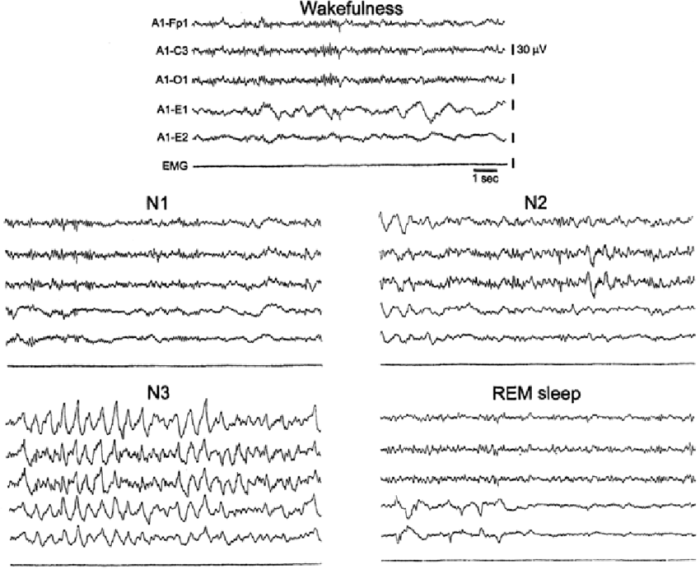
While a flat EEG is generally indicative of deep sleep, there are some situations where a flat EEG may not accurately reflect the individual’s sleep stage.
- False positives:A flat EEG can sometimes occur during periods of wakefulness, particularly in individuals with certain neurological disorders, such as epilepsy or brain injury.
- False negatives:In some cases, individuals may experience deep sleep without exhibiting a completely flat EEG. This can occur in individuals with certain sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy or sleep apnea.
4. Clinical Applications
A flat EEG has significant clinical significance in sleep studies. It is used to diagnose sleep disorders, such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy. By identifying periods of flat EEG, clinicians can determine the duration and quality of an individual’s deep sleep.
In addition to diagnosing sleep disorders, a flat EEG can also be used to monitor sleep quality and treatment effectiveness. By tracking changes in EEG patterns over time, clinicians can assess the effectiveness of sleep interventions, such as medication or behavioral therapy.
5. Future Research Directions
While there is a strong correlation between a flat EEG and deep sleep, further research is needed to better understand the relationship between these two phenomena.
- Investigate the physiological mechanisms underlying the decrease in brain activity during deep sleep.
- Identify factors that may contribute to false positives and false negatives in the relationship between flat EEG and deep sleep.
- Develop new methods for accurately assessing deep sleep using EEG recordings.
Query Resolution: A Flat Eeg Is A Good Indication Of Deep Sleep
What are the characteristics of a flat EEG?
A flat EEG is characterized by slow, high-amplitude delta waves, indicating reduced brain activity.
How does a flat EEG relate to deep sleep?
A flat EEG is a reliable indicator of deep sleep, as it reflects the brain’s transition to slow, high-amplitude delta waves during this stage of sleep.
Are there any exceptions to the relationship between a flat EEG and deep sleep?
In some cases, a flat EEG may not indicate deep sleep due to factors such as certain medications or underlying neurological conditions.