The arrows point to filaments that make up the . – The arrows point to filaments that make up the very fabric of our universe, from the grand tapestry of galaxies to the intricate workings of cells. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of filaments, uncovering their diverse roles in shaping the cosmos, celestial bodies, and even the fundamental processes of life.
Filaments, thread-like structures, permeate the solar system, shaping the magnetic fields of planets and contributing to the formation of comets. In astrophysics, they play a pivotal role in galaxy formation and evolution, guiding the flow of gas and stars. Biology reveals filaments as essential components of cells, responsible for cell division, muscle contraction, and more.
1. Filaments in the Solar System
Filaments are thin, thread-like structures observed in the solar system. They are composed of ionized gas and plasma and can extend for millions of kilometers. Filaments are often associated with the Sun’s magnetic field lines and play a significant role in shaping the structure and evolution of celestial bodies.
Prominent examples of celestial bodies with filaments include:
- The Sun: Filaments are a common feature of the Sun’s corona and play a role in the formation of solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
- Jupiter: Filaments are present in Jupiter’s magnetosphere and are thought to contribute to the planet’s auroral activity.
- Saturn: Filaments have been observed in Saturn’s magnetosphere and are associated with the planet’s magnetic field lines.
2. Filaments in Astrophysics
In astrophysics, filaments are large-scale structures composed of gas and dust. They play a crucial role in galaxy formation and evolution.
Formation and Properties of Filaments:
- Filaments form through the gravitational collapse of cold gas in the early universe.
- They are typically several million light-years in length and contain a significant fraction of the baryonic matter in the universe.
- Filaments are often associated with galaxies and galaxy clusters, providing the raw material for star formation and the growth of galaxies.
Role in Galaxy Formation and Evolution:
- Filaments serve as conduits for gas flow, transporting gas from the intergalactic medium into galaxies.
- They provide a framework for the formation of galaxies, as galaxies often form at the intersections of filaments.
- Filaments can also influence the evolution of galaxies by providing a source of fresh gas for star formation.
Significance in Understanding Large-Scale Structures:
- Filaments are key components of the cosmic web, a large-scale structure of filaments and galaxy clusters that permeates the universe.
- By studying filaments, astronomers can gain insights into the formation and evolution of the universe on the largest scales.
- Filaments help connect galaxies and galaxy clusters, providing a framework for understanding the distribution of matter in the universe.
3. Filaments in Biology
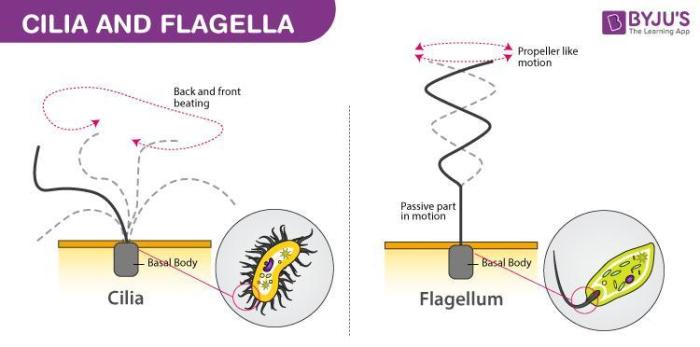
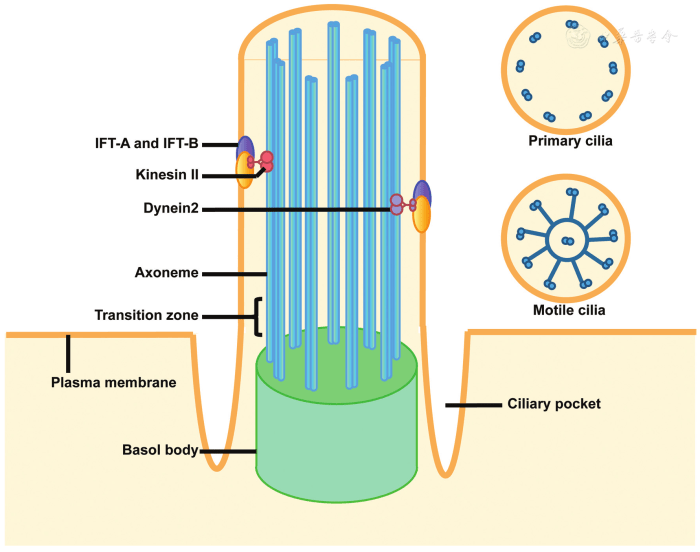
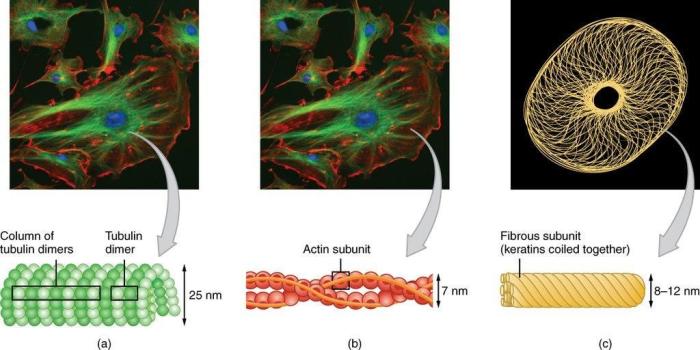
In biology, filaments are elongated, thread-like structures that perform various functions in cells.
Structure of Filaments:
- Filaments are typically composed of proteins or nucleic acids.
- They have a cylindrical shape and can be either hollow or solid.
- Filaments can be arranged in parallel bundles or form complex networks.
Types and Functions of Filaments:
- Microfilaments (actin filaments): Involved in cell motility, cell division, and muscle contraction.
- Intermediate filaments: Provide structural support to cells and tissues.
- Microtubules: Involved in cell division, intracellular transport, and maintaining cell shape.
Importance in Cellular Processes:
- Filaments play a crucial role in cell division by forming the mitotic spindle.
- They are essential for muscle contraction, enabling movement and locomotion.
- Filaments contribute to the structural integrity of cells and tissues, maintaining their shape and protecting them from mechanical stress.
4. Filaments in Materials Science

In materials science, filaments are thin, elongated fibers used in various applications.
Properties and Applications of Filaments:
- Filaments can be made from a wide range of materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics.
- They offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them suitable for lightweight structures.
- Filaments are used in composites, reinforcing materials such as plastics and metals to enhance their strength and stiffness.
- They are also employed in electronics, as conductors, resistors, and electrodes.
Advantages and Challenges:
- Advantages: High strength, low weight, flexibility, and versatility.
- Challenges: Brittleness, susceptibility to breakage, and potential for defects.
Detailed FAQs: The Arrows Point To Filaments That Make Up The .
What are filaments?
Filaments are thread-like structures found in various contexts, from astrophysics to biology.
How do filaments contribute to galaxy formation?
Filaments guide the flow of gas and stars, playing a crucial role in the formation and evolution of galaxies.
What is the role of filaments in cells?
Filaments are essential for cell division, muscle contraction, and other cellular processes.
