O2 sensor MA reading negative: a perplexing enigma that sets the stage for an exploration into the intricacies of automotive diagnostics. This reading, a deviation from the expected norm, beckons us to uncover its underlying causes, implications, and remedies, promising a journey rich in technical insights and practical solutions.
As we delve into the realm of oxygen sensors, we’ll decipher their intricate operation, unravel the significance of negative readings, and trace the potential culprits responsible for this anomaly. Through a comprehensive analysis of troubleshooting techniques, diagnostic methods, and repair strategies, we’ll empower you to conquer this automotive challenge and restore your vehicle to optimal performance.
Sensor Operation and Readings

An oxygen sensor (O2 sensor) is a critical component in the exhaust system of modern vehicles. Its primary function is to monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gas, providing real-time feedback to the engine’s electronic control unit (ECU).
The O2 sensor operates on the principle of electrochemistry. It consists of a solid electrolyte material, typically zirconia or titania, sandwiched between two electrodes: a reference electrode with a known oxygen concentration and a sensing electrode exposed to the exhaust gas.
As oxygen molecules diffuse through the electrolyte from the sensing electrode to the reference electrode, an electrical potential difference is generated between the electrodes.
O2 Sensor Output Signal
The electrical potential difference generated by the O2 sensor is directly proportional to the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. When the exhaust gas contains a high oxygen content, indicating a lean air-fuel mixture, the potential difference is positive. Conversely, when the exhaust gas contains a low oxygen content, indicating a rich air-fuel mixture, the potential difference is negative.
The ECU uses the O2 sensor’s output signal to adjust the air-fuel ratio in the engine. By maintaining the air-fuel ratio close to the stoichiometric ratio (14.7:1), the ECU ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
Significance of a Negative O2 Sensor Reading
A negative O2 sensor reading typically indicates a rich air-fuel mixture, meaning there is an excess of fuel relative to the amount of air in the combustion process. This can occur due to various factors, such as:
- Faulty fuel injector
- Clogged air filter
- Exhaust leak
- Mass airflow sensor malfunction
A rich air-fuel mixture can lead to several issues, including increased fuel consumption, decreased engine power, and elevated emissions. It is important to address a negative O2 sensor reading promptly to prevent these adverse effects and maintain optimal engine operation.
Causes of Negative Readings
Negative readings from an O2 sensor can arise from various factors, including sensor malfunction and engine conditions. Understanding these causes helps diagnose and resolve the issue.
If you’re getting negative O2 sensor MA readings, it’s worth considering the type of dozer you’re using. High-track dozers are better suited for rough terrain, while low-track dozers are ideal for flat surfaces. Understanding the differences between these two types of dozers can help you troubleshoot your O2 sensor issues and get your machine running smoothly again.
Sensor Failure
- Sensor Shorting:An internal short within the sensor can create a negative voltage bias, leading to negative readings.
- Damaged Sensor Element:Physical damage to the sensor element, such as cracks or contamination, can alter its response and result in negative readings.
Engine Conditions
Certain engine conditions can also contribute to negative O2 sensor readings:
- Rich Fuel Mixture:An excessively rich fuel mixture can create a reducing atmosphere in the exhaust, causing the sensor to produce a negative voltage.
- Exhaust Leaks:Leaks in the exhaust system before the O2 sensor can introduce fresh air, affecting the sensor’s readings and potentially causing negative values.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics

Identifying the cause of a negative O2 sensor reading requires a systematic approach. This involves understanding the sensor’s operation, potential causes of negative readings, and employing specific diagnostic techniques.
Diagnostic Steps
- Visual Inspection:Check for any physical damage to the sensor, wiring, or connector.
- Data Monitoring:Use a scan tool or diagnostic equipment to observe live O2 sensor data and identify any abnormal readings.
- Sensor Testing:Employ specialized tools like an oscilloscope or multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage output and response time.
- Circuit Testing:Inspect the electrical circuit associated with the O2 sensor, including the wiring harness, ground connections, and power supply.
- Fuel Trim Analysis:Analyze the fuel trim data from the engine control module (ECM) to determine if the negative O2 sensor reading is affecting fuel mixture adjustments.
Interpreting Diagnostic Results, O2 sensor ma reading negative
The diagnostic results will help determine the underlying cause of the negative O2 sensor reading. Common issues include:
- Sensor failure
- Wiring or connector problems
- Exhaust system leaks
li>Faulty fuel injector
Once the root cause is identified, appropriate repairs can be made to restore proper O2 sensor operation and ensure accurate fuel mixture control.
Effects on Engine Performance: O2 Sensor Ma Reading Negative
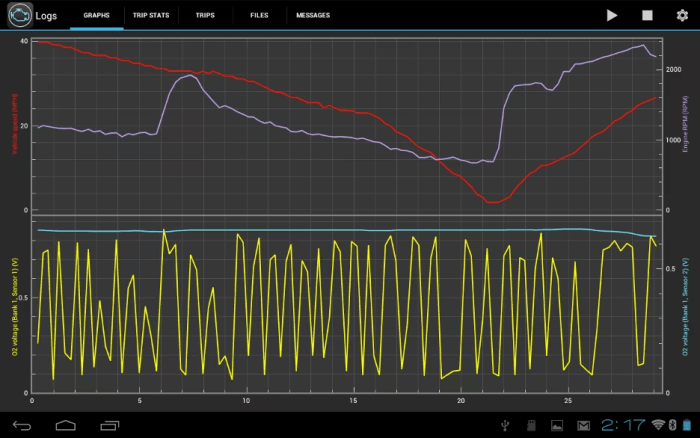
A negative O2 sensor reading can have significant effects on engine performance. When the O2 sensor reading is negative, the engine control module (ECM) interprets this as an excessively rich air-fuel mixture. In response, the ECM will reduce the fuel injector pulse width, causing the engine to run leaner.
A lean air-fuel mixture can lead to several problems, including:
- Reduced engine power and torque
- Increased fuel consumption
- Increased emissions
- Engine damage
Ignoring a negative O2 sensor reading can lead to serious consequences. The lean air-fuel mixture can cause the engine to run hot, which can damage the pistons, valves, and other engine components. In addition, the increased emissions can lead to environmental problems.
Repair and Maintenance
Maintaining a functional O2 sensor is crucial for optimal engine performance. If a negative reading persists, it’s essential to replace the faulty sensor promptly.
Replacement Procedures
Replacing an O2 sensor involves the following steps:
- Locate the sensor and disconnect its electrical connector.
- Use a wrench to unscrew the old sensor from the exhaust pipe.
- Apply anti-seize compound to the threads of the new sensor.
- Screw in the new sensor by hand until it’s snug.
- Tighten the sensor using a torque wrench according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
Importance of Quality and Installation
Using high-quality O2 sensors is paramount to ensure accurate readings and longevity. Proper installation techniques are equally important to prevent leaks or damage that can affect sensor performance.
Maintenance Tips
To prevent future negative readings, consider the following maintenance tips:
- Avoid using leaded gasoline, as it can damage the sensor.
- Inspect the sensor regularly for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Clean the sensor using a suitable solvent if it becomes contaminated.
- Consider replacing the sensor every 60,000 to 90,000 miles to maintain optimal performance.
Questions Often Asked
What causes a negative O2 sensor reading?
Negative O2 sensor readings can be attributed to various factors, including sensor failure, engine conditions such as lean air-fuel mixtures, or exhaust leaks.
How can I troubleshoot a negative O2 sensor reading?
Troubleshooting involves visual inspection of the sensor and wiring, testing sensor resistance and voltage output, and analyzing engine data using diagnostic tools.
What are the consequences of ignoring a negative O2 sensor reading?
Ignoring negative O2 sensor readings can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.